Preparing to Hack Wi-Fi
Jul 24, 2019 Wifi Hacker, a New Wifi Hacking tool and method discovered to hack wifi password WPA/WPA2 enabled WiFi networks that allow WiFi Hackers to gain PSK. Using the above method now WiFi Hackers can hack the WiFi Password with the help of Wifi hackers app and other hacking apps that primarily used by hackers to attack wifi networks and hack the wifi connected devices. Basically, cracking WPA (2) under Windows works as follows: Run Wireshark with your WiFi being set to promiscious mode Capture the full initial 4-way-handshake (since this is the only traffic that gets encrypted by the WPA-PSK) and save the capture file in 'pcap format'. Jul 25, 2017 Crack WPA/WPA2 Wi-Fi Routers with Airodump-ng and Aircrack-ng/Hashcat. This is a brief walk-through tutorial that illustrates how to crack Wi-Fi networks that are s ecured using weak passwords. Linux's wpasupplicant v2.6 is also vulnerable to the installation of an all-zero encryption key in the 4-way handshake. This was discovered by John A. As a result, all Android versions higher than 6.0 are also affected by the attack, and hence can. Step By Step Hack WPA/WPA2 Wi Fi Passwords Using Aircrack Ng Next Page In this tutorial I will tell you how to crack wpa/wpa2 wi-fi in kali linux using aircrack-ng.

- Understand when you can legally hack Wi-Fi. In most regions, the only time you can hack a WPA or WPA2 network is when the network either belongs to you or belongs to someone who has given you explicit consent to hack the network.
- Hacking networks that don’t meet the above criteria
is illegal, and may constitute a federal crime.
- Hacking networks that don’t meet the above criteria
- Download the Kali Linux disk image. Kali Linux is the preferred tool for hacking WPA and WPA2. You can download the Kali Linux installation image (ISO) by doing the following:
- Go to https://www.kali.org/downloads/ in your computer’s web browser.
- Click HTTP next to the version of Kali you want to use.
- Wait for the file to finish downloading.
- Attach a flash drive to your computer. You’ll need to use a flash drive with at least 4 gigabytes of space for this process.
- Make your flash drive bootable. This is necessary in order to be able to use the USB flash drive as an installation location.
- You can also use a Mac for this step.
- Place the Kali Linux ISO file on the flash drive. Open the flash drive, then drag the downloaded Kali Linux ISO file into the flash drive’s window.
- Make sure you leave your USB flash drive plugged in after you finish this process.
- Install Kali Linux. To install Kali Linux on your computer, do the following:
- Prompt your Windows computer to restart.
- Enter the BIOS menu.
- Set your computer to start from your USB drive by finding the “Boot Options” (or similar) section, selecting your USB drive’s name, and moving it to the top of the list.
- Save and exit, then wait for the Kali Linux installation window to appear (you may have to restart your computer one more time).
- Follow the Kali Linux installation prompts.
- Buy a Wi-Fi card that supports monitoring. You can find Wi-Fi cards online or in tech department stores. Make sure that your Wi-Fi card allows monitoring (RFMON), or you won’t be able to hack a network.
- Many computers have built-in RFMON Wi-Fi cards, so you might want to try the first four steps of the next part before buying one.
- If you’re using Kali Linux in a virtual machine, you will need a Wi-Fi card regardless of your computer’s card.
- Log into your Kali Linux computer as root. Enter your root username and password when logging in.
- You will need to be on your root account at all times during the hacking process.
- Plug your Wi-Fi card into your Kali Linux computer. Doing so will immediately prompt the card to begin setting up and downloading drivers for itself; if prompted, follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup. Once you’re done with this step, you can proceed with hacking your selected network.
- If you’ve already set up the card on your computer before, you’ll still have to set it up for Kali Linux here by plugging it in.
- In most cases, simply attaching the card to your computer will be enough to set it up.
Part2 Hacking Wi-Fi
- Open your Kali Linux computer’s Terminal. Find and click the Terminal app icon, which resembles a black box with a white “>_” on it.
- You can also just
press Alt+Ctrl+Tto open the Terminal.
- You can also just
- Enter the Aircrack-ng installation command. Type in the following command, then press ↵ Enter:
sudo apt-get installaircrack -ng - Enter your password when prompted. Type in the password you use to log into your computer, then press ↵ Enter. This enables root access for any other commands executed in Terminal.
- If you open another Terminal window (as you may later in this article), you may have to run a command with the
sudo prefix and/or enter your password again.
- If you open another Terminal window (as you may later in this article), you may have to run a command with the
- Install Aircrack-ng. Press Y when prompted, then wait for the program to finish installing.
- Turn on
airmon -ng. Type in the following command, thenpress ↵ Enter.airmon -ng - Find the monitor name. You’ll find this in the “Interface” column.
- If you’re hacking your own network, it will usually be named “wlan0”.
- If you don’t see a monitor name, your Wi-Fi card doesn’t support monitoring.
- Begin monitoring the network. You can do so by typing in the following command and pressing ↵ Enter:
airmon -ng start wlan0- Make sure you replace “wlan0” with the name of your target network if it’s different.
- Enable a monitor mode interface. Enter the following command:
iwconfig - Kill any processes that return errors. In some cases, your Wi-Fi card will conflict with running services on your computer. You can kill these processes by entering the following command: airmon-ng check kill
- Review the monitor interface name. In most cases, the name will be something like “mon0” or “wlan0mon”.
- Tell your computer to listen to nearby routers. To get a list of all routers in range, enter the following command:
airodump -ng mon0- Make sure you replace “mon0” with whatever your monitor interface name was in the last step.
- Find the router you want to hack. At the end of each string of text, you’ll see a name; find the one belonging to the network you want to hack into.
- Make sure the router is using WPA or WPA2 security. If you see “WPA” or “WPA2” immediately to the left of the network’s name, you can proceed; otherwise, you cannot hack the network.
- Note the MAC address and channel number of the router. These pieces of information are to the left of the network’s name:
- MAC address — This is the line of numbers on the
far-left side of your router’s line. - Channel — This is the number (e.g., 0, 1, 2, etc.) directly to the left of the WPA or WPA2 tag.
- MAC address — This is the line of numbers on the
- Monitor your selected network for a handshake. A “handshake” occurs when an item connects to a network (e.g., when your computer connects to a router). Enter the following code, making sure to replace the necessary components of the command with your network’s information:
airodump -ng -c channel —bssid MAC -w /root/Desktop/ mon0- Replace “channel” with the channel number you found in the last step.
- Replace “MAC” with the MAC address you found in the last step.
- Remember to replace “mon0” with whatever your interface name was.
- Here’s an example address:
airodump -ng -c 3 —bssid 1C:1C:1E:C1:AB:C1 -w /root/Desktop/ wlan0mon
- Wait for a handshake to appear. Once you see a line with the tag “WPA handshake:” followed by a MAC address in the upper-right corner of the screen, you can proceed.
- If you’re not in a waiting mood, you can force a handshake using a
deauth attackbefore continuing with this part.
- If you’re not in a waiting mood, you can force a handshake using a
- Exit
airodump -ng, then open the desktop. Press Ctrl+C to quit, then make sure you can see the “.cap” file on your computer’s desktop. - Rename your “.cap” file. While not strictly necessary, this will make it easier to work with later. Enter the following command to change the name, making sure to replace “name” with whatever you want to name the file: mv ./-01.cap name
.cap - If your “.cap” file isn’t named “-01.cap”, replace “-01.cap” with whatever your “.cap” file’s name is.
- Convert the “.cap” file into “.hccapx” format. You can do this by using Kali Linux’s converter. Enter the following command, making sure to replace “name” with your file’s name: cap2hccapx.bin name
.cap name.hccapx - You can also go to https://hashcat.net/cap2hccapx/ and upload the “.cap” file to the converter by clicking Choose File and selecting your file. Once the file is uploaded, click Convert to convert it and then download it back onto your desktop before proceeding.
- Install naive-
hashcat . This is the service you’ll use to crack the password. Enter the following commands in order:sudo git clone https://github.com/brannondorsey/naive-hashcat cd naive-hashcat curl -L -o dicts/rockyou.txt https://github.com/brannondorsey/naive-hashcat/releases/download/data/rockyou.txt- If your computer doesn’t have a GPU, you’ll need to use
aircrack -ng instead.
- If your computer doesn’t have a GPU, you’ll need to use
- Run naive-
hashcat . Once it finishes installing, enter the following command (making sure to replace any instance of “name” with your “.cap” file’s name): HASH_FILE=name.hccapx POT_FILE=name.pot HASH_TYPE=2500 ./naive-hashcat .sh - Wait for the network password to be cracked. Once the password is cracked, its string will be added to the “name.pot” file found in the “naive-
hashcat ” directory; the word or phrase after the last colon in the string is the password.- It can take anywhere from a few hours to a few months for the password to be cracked.
Part 3 Using Aircrack-Ng for Non-GPU Computers
- Download a dictionary file. The most commonly used dictionary file is “Rock You”. You can download it by entering the following command: curl -L -o rockyou.txt https://github.com/brannondorsey/naive-hashcat/releases/download/data/rockyou.txt
- Keep in mind that aircrack-ng will not be able to crack the WPA or WPA2 password if the password isn’t in the word list.
- Tell aircrack-ng to begin cracking the password. Enter the following command, making sure to use the necessary network information when doing so: aircrack-ng -a2 -b MAC -w rockyou.txt name
.cap - If you’re cracking a WPA network instead of a WPA2 network, replace “-a2” with -a.
- Replace “MAC” with the MAC address you found in the last section.
- Replace “name” with your “.cap” file’s name.
- Wait for Terminal to display the results. When you see a “KEY FOUND!” heading
appear ,aircrack -ng has found the password. You’ll see the password displayed in brackets to the right of the “KEY FOUND!” heading.
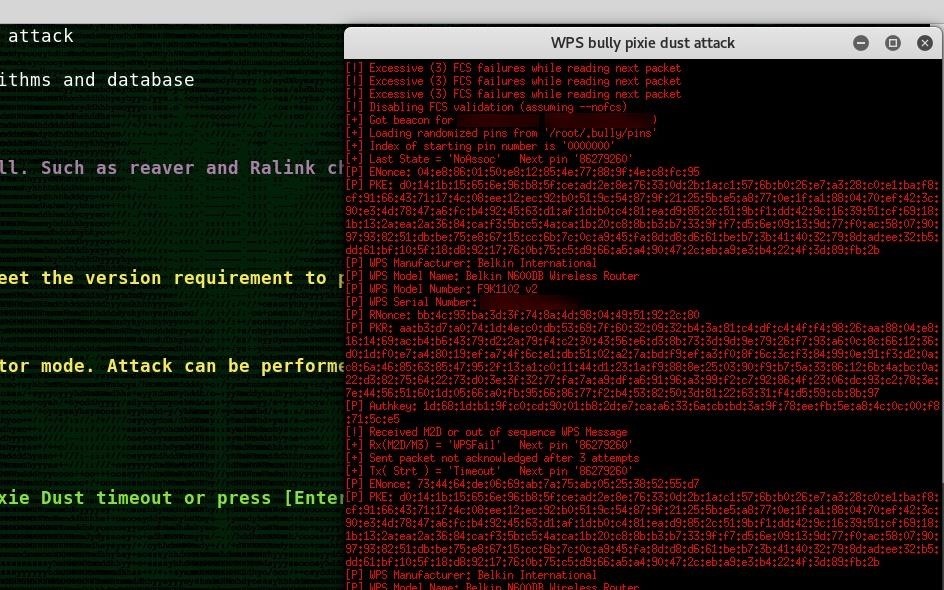
Part 4 Using Deauth Attacks to Force a Handshake
- Understand what a
deauth attack does.Deauth attacks send maliciousdeauthentication packets to the router you’re trying to break into, causing the Internet to disconnect and ask the Internet user to log back in. Once the user logs back in, you will be provided with a handshake. - Monitor your network. Enter the following command, making sure to enter your network’s information where necessary:
airodump -ng -c channel —bssid MAC- For example:
airodump -ng -c 1 —bssid 9C:5C:8E:C9:AB:C0
- For example:
- Wait for something to connect to the network. Once you see two MAC addresses appear next to each other (and a string of text that includes a manufacturer name next to them), you can proceed.
- This indicates that a client (e.g., a computer) is now connected to the network.
- Open a new Terminal window. You can just press Alt+Ctrl+T to do this. Make sure
airodump -ng is still running in the background Terminal window. - Send the
deauth packets. Enter the following command, making sure to substitute your network’s information:aireplay -ng -0 2 -a MAC1 -c MAC2 mon0- The “2” refers to the number of packets to send. You can increase or decrease this number, but keep in mind that sending more than two packets can cause a noticeable security breach.
- Replace “MAC1” with the left-most MAC address at the bottom of the background Terminal window.
- Replace “MAC2” with the right-most MAC address at the bottom of the background Terminal window.
- Remember to replace “mon0” with your interface name that you found when your computer initially looked for routers.
- An example command looks like this:
aireplay -ng -0 3 -a 9C:5C:8E:C9:AB:C0 -c 64:BC:0C:48:97:F7 mon0
- Re-open the original Terminal window. Go back to the background Terminal window when you’re done sending the
deauth packets. - Look for a handshake. Once you see the “WPA handshake:” tag and the address next to it, you can proceed with hacking your network.
Source: WikiHow
Wireless networks are accessible to anyone within the router’s transmission radius. This makes them vulnerable to attacks. Hotspots are available in public places such as airports, restaurants, parks, etc.
In this tutorial, we will introduce you to common techniques used to exploit weaknesses in wireless network security implementations. We will also look at some of the countermeasures you can put in place to protect against such attacks.
Topics covered in this tutorial
What is a wireless network?
A wireless network is a network that uses radio waves to link computers and other devices together. The implementation is done at the Layer 1 (physical layer) of the OSI model.
How to access a wireless network?
You will need a wireless network enabled device such as a laptop, tablet, smartphones, etc. You will also need to be within the transmission radius of a wireless network access point. Most devices (if the wireless network option is turned on) will provide you with a list of available networks. If the network is not password protected, then you just have to click on connect. If it is password protected, then you will need the password to gain access.
Wireless Network Authentication
Since the network is easily accessible to everyone with a wireless network enabled device, most networks are password protected. Let’s look at some of the most commonly used authentication techniques.
WEP
WEP is the acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy. It was developed for IEEE 802.11 WLAN standards. Its goal was to provide the privacy equivalent to that provided by wired networks. WEP works by encrypting the data been transmitted over the network to keep it safe from eavesdropping.
WEP Authentication
Open System Authentication (OSA) – this methods grants access to station authentication requested based on the configured access policy.
Shared Key Authentication (SKA) – This method sends to an encrypted challenge to the station requesting access. The station encrypts the challenge with its key then responds. If the encrypted challenge matches the AP value, then access is granted.
WEP Weakness
Hack Wpa2 Wifi Passwords Apk
WEP has significant design flaws and vulnerabilities.
- The integrity of the packets is checked using Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC32). CRC32 integrity check can be compromised by capturing at least two packets. The bits in the encrypted stream and the checksum can be modified by the attacker so that the packet is accepted by the authentication system. This leads to unauthorized access to the network.
- WEP uses the RC4 encryption algorithm to create stream ciphers. The stream cipher input is made up of an initial value (IV) and a secret key. The length of the initial value (IV) is 24 bits long while the secret key can either be 40 bits or 104 bits long. The total length of both the initial value and secret can either be 64 bits or 128 bits long.The lower possible value of the secret key makes it easy to crack it.
- Weak Initial values combinations do not encrypt sufficiently. This makes them vulnerable to attacks.
- WEP is based on passwords; this makes it vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
- Keys management is poorly implemented. Changing keys especially on large networks is challenging. WEP does not provide a centralized key management system.
- The Initial values can be reused
Because of these security flaws, WEP has been deprecated in favor of WPA
WPA
WPA is the acronym for Wi-Fi Protected Access. It is a security protocol developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance in response to the weaknesses found in WEP. It is used to encrypt data on 802.11 WLANs. It uses higher Initial Values 48 bits instead of the 24 bits that WEP uses. It uses temporal keys to encrypt packets.
WPA Weaknesses
- The collision avoidance implementation can be broken
- It is vulnerable to denial of service attacks
- Pre-shares keys use passphrases. Weak passphrases are vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
How to Crack Wireless Networks
WEP cracking
Cracking is the process of exploiting security weaknesses in wireless networks and gaining unauthorized access. WEP cracking refers to exploits on networks that use WEP to implement security controls. There are basically two types of cracks namely;
- Passive cracking– this type of cracking has no effect on the network traffic until the WEP security has been cracked. It is difficult to detect.
- Active cracking– this type of attack has an increased load effect on the network traffic. It is easy to detect compared to passive cracking. It is more effective compared to passive cracking.
WEP Cracking Tools
- Aircrack– network sniffer and WEP cracker. Can be downloaded from http://www.aircrack-ng.org/
- WEPCrack– this is an open source program for breaking 802.11 WEP secret keys. It is an implementation of the FMS attack. http://wepcrack.sourceforge.net/
- Kismet- this can include detector wireless networks both visible and hidden, sniffer packets and detect intrusions. https://www.kismetwireless.net/
- WebDecrypt– this tool uses active dictionary attacks to crack the WEP keys. It has its own key generator and implements packet filters. http://wepdecrypt.sourceforge.net/
WPA Cracking
WPA uses a 256 pre-shared key or passphrase for authentications. Short passphrases are vulnerable to dictionary attacks and other attacks that can be used to crack passwords. The following tools can be used to crack WPA keys.
- CowPatty– this tool is used to crack pre-shared keys (PSK) using brute force attack. http://wirelessdefence.org/Contents/coWPAttyMain.htm
- Cain & Abel– this tool can be used to decode capture files from other sniffing programs such as Wireshark. The capture files may contain WEP or WPA-PSK encoded frames. https://www.softpedia.com/get/Security/Decrypting-Decoding/Cain-and-Abel.shtml
General Attack types
- Sniffing– this involves intercepting packets as they are transmitted over a network. The captured data can then be decoded using tools such as Cain & Abel.
- Man in the Middle (MITM) Attack– this involves eavesdropping on a network and capturing sensitive information.
- Denial of Service Attack– the main intent of this attack is to deny legitimate users network resources. FataJack can be used to perform this type of attack. More on this in article
Cracking Wireless network WEP/WPA keys
It is possible to crack the WEP/WPA keys used to gain access to a wireless network. Doing so requires software and hardware resources, and patience. The success of such attacks can also depend on how active and inactive the users of the target network are.
We will provide you with basic information that can help you get started. Backtrack is a Linux-based security operating system. It is developed on top of Ubuntu. Backtrack comes with a number of security tools. Backtrack can be used to gather information, assess vulnerabilities and perform exploits among other things.
Hack Wpa Passwords
Some of the popular tools that backtrack has includes;
Hack Wpa2 Wifi Password Windows
- Metasploit
- Wireshark
- Aircrack-ng
- NMap
- Ophcrack
Cracking wireless network keys requires patience and resources mentioned above. At a minimum, you will need the following tools
A wireless network adapter with the capability to inject packets (Hardware)
- Kali Operating System. You can download it from here https://www.kali.org/downloads/
- Be within the target network’s radius. If the users of the target network are actively using and connecting to it, then your chances of cracking it will be significantly improved.
- Sufficient knowledge of Linux based operating systems and working knowledge of Aircrack and its various scripts.
- Patience, cracking the keys may take a bit of sometime depending on a number of factors some of which may be beyond your control. Factors beyond your control include users of the target network using it actively as you sniff data packets.
How to Secure wireless networks
Hack Wpa Kali
In minimizing wireless network attacks; an organization can adopt the following policies
- Changing default passwords that come with the hardware
- Enabling the authentication mechanism
- Access to the network can be restricted by allowing only registered MAC addresses.
- Use of strong WEP and WPA-PSK keys, a combination of symbols, number and characters reduce the chance of the keys been cracking using dictionary and brute force attacks.
- Firewall Software can also help reduce unauthorized access.
Hacking Activity: Crack Wireless Password
In this practical scenario, we are going touse Cain and Abel to decode the stored wireless network passwords in Windows. We will also provide useful information that can be used to crack the WEP and WPA keys of wireless networks.
Decoding Wireless network passwords stored in Windows
- Download Cain & Abel from the link provided above.
- Open Cain and Abel
- Ensure that the Decoders tab is selected then click on Wireless Passwords from the navigation menu on the left-hand side
- Click on the button with a plus sign
Hack Wpa Wps Wifi By Linux
- Assuming you have connected to a secured wireless network before, you will get results similar to the ones shown below
- The decoder will show you the encryption type, SSID and the password that was used.
Summary
Hack Wpa Wifi
- Wireless network transmission waves can be seen by outsiders, this possesses many security risks.
- WEP is the acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy. It has security flaws which make it easier to break compared to other security implementations.
- WPA is the acronym for Wi-Fi Protected Access. It has security compared to WEP
- Intrusion Detection Systems can help detect unauthorized access
- A good security policy can help protect a network.