exhibited at Museum of Making Music
- Piano Lookup By Serial Number
- Gulbransen Piano Serial Number Lookup
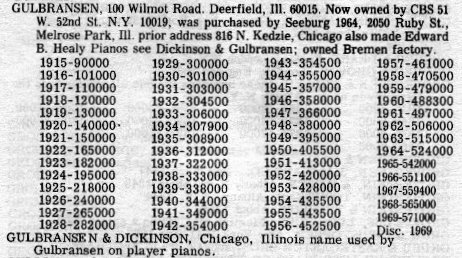
- Gulbransen Piano Company
- Used Gulbransen Piano Values
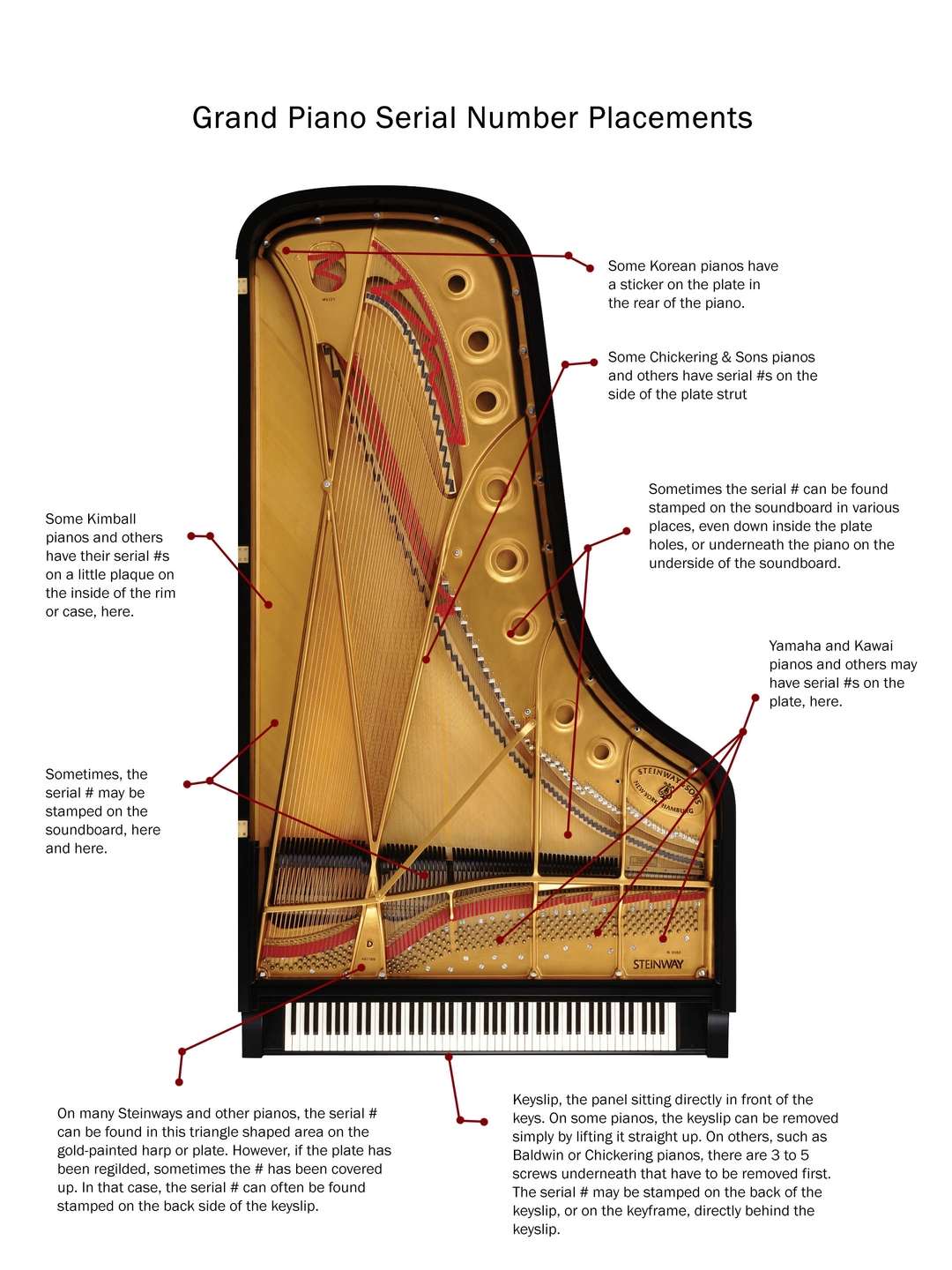
Once you know the name brand of your piano, you will need to find the serial number. Step 1: The serial number is usually found on the plate of the piano between the bass and tenor strings. It can also be found on the top of the piano when you open the lid on Upright Pianos. You are looking for a number like those shown here. After locating the serial number on your piano, we can help you research its age and value. CLICK HERE TO DISCOVER YOUR PIANO'S AGE CLICK HERE TO DISCOVER YOUR PIANO. The piano itself was real value when compared to others of the day. Gulbransen (and M. Schulz, #2) made more actions than any factory during the 'Twenties, there in Chicago. The largest piano factory ever was built by Gulbransen and it allowed trains to enter in order to load the piano crates, since export was also a major activity. View Links to resources for the Piano Industry.
electronic home organ
Gulbransen Company was a musical instrument manufacturer of player pianos and home organs in the United States. It also made reed organs. It was originally established in 1904 by Axel Gulbransen as Gulbransen Piano Company.[1][2]
In the history of musical instruments, Gulbransen is notable for several innovations. In its early years, Gulbransen made the first upright piano with a player piano mechanism in the same case. In the 1920s, thousands of player pianos were manufactured by the firm under the Gulbransen and Dickinson name.[1] In the electronic organ era, Gulbransen pioneered several innovations in the production of home electronic organs that became industry standards:[2]
- Built-in Leslie speaker system
- Chime stop and Piano stop
- Automatic rhythm (built-in drum machine)
- Automatic walking bass (bass accompaniment)

In 1957, Gulbransen released the first transistorizedelectric organ 'Gulbransen Model B' (Model 1100),[2] although its use of transistors was limited to the tone generators, and vacuum tubes were still used for the power amplifier. (The first fully transistorized organ for churches was later built by Rodgers Instruments.)
Also in the 1960s, Gulbransen released one of the earliest transistorized rhythm machines 'Seeburg/Gulbransen Select-A-Rhythm',[4][5] collaborating with Seeburg Corporation.Note that Seeburg invented a fully transistorized rhythm machine in 1964, which was patented in 1967.[6]
On the other hand, the owner of Gulbransen has changed several times since the 1950s. Around 1950, it was sold to CBS, then in 1964, merged with Seeburg Corporation, and production was once ceased in 1969.[1] In 1985, Mission Bay Investments acquired the brand and produced Elka organs under the Gulbransen name.[2] In 2002 or 2003,[7] QRS Music Technologies acquired the brand and pianos were made by Samick.[1]
Piano Lookup By Serial Number
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ abcdJames Grebe (2011). 'The Gulbransen Piano Company'. Yesterday Once More Publications.
- ^ abcd'The Gulbransen Organ'. TheatreOrgans.com. May 2006. Includes 1957 brochures of 'Gulbransen Model B organ'.
- ^'Rare Early Seeburg Rhythm Prince Synthesizer Drum Synth'. MatrixSynth. May 13, 2009.
- ^ ab'Select-a-Rhythm Vintage Drum Machine'. EricArcher.net. Archived from the original on 2011-09-16. Retrieved 2011-11-20.
- ^Seeburg Portable Select-A-Rhythm Service Manual(PDF). Seeburg Sales Corporation. Archived from the original(PDF) on 2012-04-25.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link) Rhythm patterns were electronically generated by a 48-step binary counter using 6-stage flip-flops.
- ^US patent 3,358,068, Richard H. Campbell, Jr., Gilford, N.H. (assigned to Seeburg Corporation), 'Musical Instruments', issued 1967-12-12
— related patents filed at the same time were: Automatic Rhythm Device, Automatic Repetitive Rhythm Instrument Timing Circuitry, and sound circuits of Snare Drum Instrument and Cow Bell Instrument. - ^'QRS acquires Gulbransen: plans new types of reproducing technologies. (Industry Forefront)', Music Trades (March 1, 2003), archived from the original on 2016-04-13,
QRS Music Technologies, Inc., has acquired Gulbransen, Inc., ...
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gulbransen Company. |

Gulbransen Piano Serial Number Lookup
- www.qrsmusic.com — Gulbransen history at QRS Music Technologies, Inc.
Gulbransen Piano Company
