Related: English TensesEnglish Tenses TableEnglish Tenses ExercisesEnglish Tenses PdfEnglish Tenses übungenEnglish Tenses QuizEnglish Tenses ChartEnglish Tenses übersicht
- What Are The 16 Tenses In English
- 16 Tenses In English Grammar Chart
- English Tenses
- 16 Tenses In English Grammar Worksheet
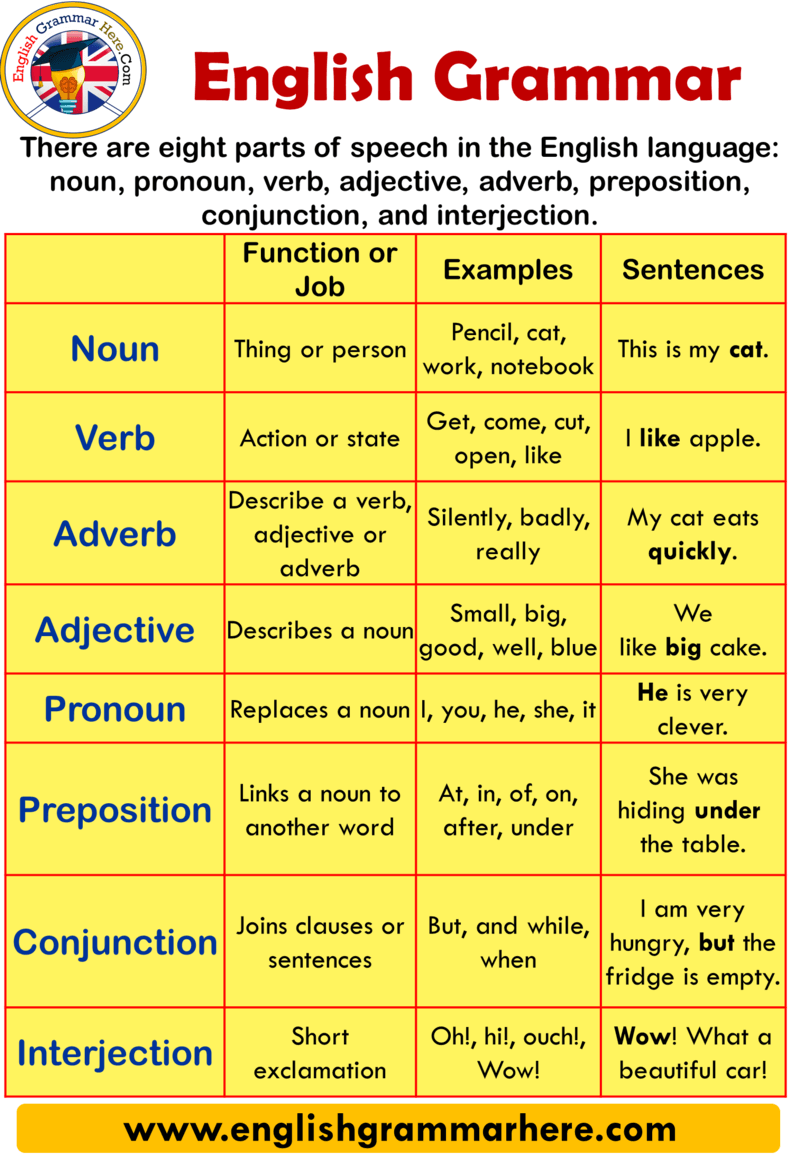
- Tag: tenses in english grammar.
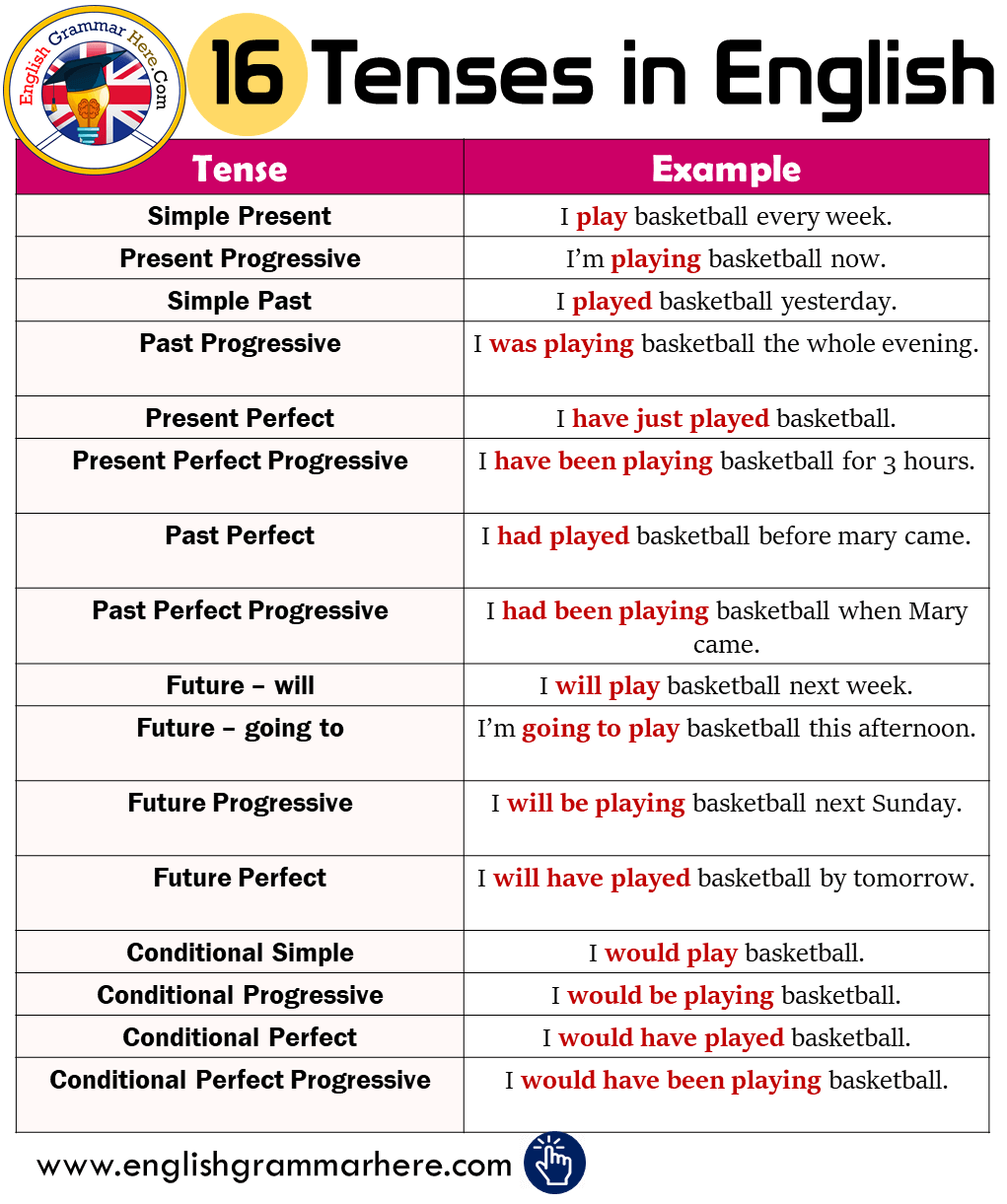
- 16 Tenses in English Grammar (Formula and Examples. Basic English Verb Tenses and Usage Tips.
- All of these sixteen sentence patterns (often called the 16 tenses) are possible. The table below shows how each part can be added, in either the past tense or present tense. English Tense Table: The possible combinations of the 4 basic parts.
Complete English Grammar Tenses in Hindi + Free PDF: Get fully detailed English grammar tenses in Hindi with chart and step by step rules + free pdf to download.
7esl.com'> pinimg.com'>
pinimg.com'>CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Tenses are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English. Here we have given CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Tenses.
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Tenses
1. Read the following sentences carefully :
- Birds fly in the air.
- My brother flew to England last week.
- I shall fly a kite on Sunday. –
In the first sentence the Verb ‘fly’ refers to the Present time, in the second sentence the Verb ‘flew’ refers to the action in the Past, while the Verb in the third sentence ‘shall fly’ refers to the Future.
2. The Tense of a Verb shows the time when an action takes place.
There are three Tenses :
I. Present Tense
II. Past Tense
III. Future Tense
3. In order to show at what stage an action is, each of the three tenses has been sub-divided into four heads. These sub-divisions are—
| Tense | Indefinite | Continuous or Progressive | Perfect | Perfect |
| Present | I play | I am playing | I have played | I have been playing |
| Past | I played | I was playing | I had played | I had been playing |
| Future | I shall play | I shall be playing | I shall have played | I shall have been playing |
Thus, the tense of a verb does not show the time of an action or event alone. It shows the state of that action also.
I. The Present Tense
A. Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present is used to express :
(i) A habitual action
(ii) A general truth
(iii) What is happening (in exclamatory sentences only)
(iv) An order or request.
(i) A habitual action :
I go for a walk daily.
He comes to school at 8 O’clock.
(ii) General truth :
The sun rises in the east.
Two and two make four.
(iii) What is happening :
Here comes the chief guest !
(iv) An order or request :
Obey your teachers.
Exercise 1
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks in the following with the correct form of the verb given in (Present Tense)
1. I ……… in Model Town. (live)
2. The mother ……… food for us. (cook)
3. She ……. to temple every morning. (go)
4. He ……… on me whenever he wants. call)
5. I …….. what my sister (eat)
6. My father …………. from his office in the evening. (return)
7. They …………. football every evening. (play)
8. I …………. everybody well. (wish)
9. The cat …………. rats. (kill)
10. The farmers ………….. rain. (need)
Answers:
1. live
2. cooks
3. goes
4. call
5. eat, eats
6. returns
7. play
8. wish
9. kills
10. need
B. Present Continuous Tense
(Is/am/are + Verb + ing)
(i) In order to form the Present Continuous Tense, we add Present Participle to is, am or are. The Present Participle is formed by adding ‘ing’ to the first form of the verb.
‘Is’ is used with he, she, it or Third Person Singular Noun, ‘am is used with T and ‘are’ is used with we, you, they and plural Nouns.
Examples: She is singing a song.
(ii) In Interrogative form, the helping verb is used before the subject.
[Is/am/are + Subject + (Verb + ing)……….. ?]
Examples : Are you going home ?
(iii) In Negative form, we add ‘not between the Principal Verb and the operative helping verb.
[Subject + is/am/are + not + (Verb + ing) …]
Examples: She is not weeping.
Uses of the Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense is used with the words—at this time, at present, at the moment, now, nowadays, still etc. and in the following cases :
(a) To describe an action in progress and/or the continuity of the action.
The girls are singing a chorus.
(b) To describe an action in progress, but not necessarily at the time of speaking.
India is exporting onions to the Middle East.
What are you writing these days ?
Exercise 2
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets :
1. Look ! the sun ………… (rise)
2. Why ……….. you ………….. so fast ? (run)
3. The children ………. .in the park. (play)
4. Mohini ……….. a novel now. (read)
5. Water …………. from the running tap. (flow)
6. …………… it ………… outside now ? (rain)
7. What …………. your sister these days ? (do)
8. I ………… tonight. (return)
9. They …………… for Kanpur tomorrow. (leave)
10. Why ………… you ……….. a noise ? (make)
Answers
1. is rising
2. are, running
3. are playing
4. is reading
5. is flowing
6. Is, raining
7. is, doing
8. am returning
9. are leaving
10. are, making
C. Present Perfect Tense
(Subject + Has /have + III form of the verb)
(i) In the Present Perfect Tense the past participle (III) form of the verb is used with has or have. ‘Has’ is added with third person singular subjects, as—‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’ and ‘Have’ is added with T, ‘we’, ‘you, ‘they’ and plural nouns.
He has won a prize.
You have insulted me.
I have taken the dose of medicine.
(ii) In Interrogative form [Has, have are placed before the subject.]
(Has/have + Subject + III form of the Verb…?)
Have they crossed the river ?
Where have you seen my brother ?
(iii) In Negative form [‘not’ is used between the main verb and the helping verb.]
(Subject + has/have + not + III form of the Verb…)
She has not come yet.
I have not received any information.
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used with the words : yet, as yet, already, just, just now, so far, since, ever since, presently, once, twice, thrice etc. and in the following cases :
(a) To express an action that has been recently completed.
I have just received the letter.
(b) To describe an action the time of which is not given.
The train has steamed in.
(c) To describe a past experience.
I have seen this picture several times.
(d) To express an action that began in the Past and still continues.
He has worked in this school for five years, (is still working)
Exercise 3
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense (present) of the verbs given in brackets :
1. Where ………… you ………… your purse ? (lose)
2. ………… she not yet her work ? (finish)
3. How many sums ………… she ………… ? (solve)
4. My sister ………… from Meerut presently. (return)
5. Raju ………… Saroj since 1980. (know)
6. Asha ………… never ………… the Red Fort. (see)
7. ………… you not ………… your bath as yet ? (take)
8. I ………… not ………… my lesson. (revise)
9. We ………… not ………… from Rajni for the last four months. (hear)
10. She ………… in Delhi for eight years. (live)
Answers:
1. have, lost
2. Has, finished
3. has. solved
4. has returned
5. has known
6. has, seen
7. Have, taken
8. have, revised
9. have, heard
10. has lived
D. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
[Subject + has/have + been + I form of the Verb + ing…)
In order to form the Present Perfect Continuous Tense, we put has been or have been before the Present Participle Form of the Verb ; as—
It has been raining for two hours.
I have been flying a kite since 2 O’clock.
(a) The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe an action that began in the Past, is still continuing and may extend into the Future ; as—
She has been waiting for you for three hours.
They have been playing cards since 10 A.M.
(b) This tense is also used to express an action in a sentence which begins with ‘For how long or ‘Since when’, as in—
For how long have you been sitting here ?
Since when has he been living in this house ?
(c) This tense is also used to express an action which began in the past and has been just completed. However, its result is visible in the present, as in—
I have been studying since morning and I am much tired now.
She has been washing the dishes for an hour and her clothes are dirty now.
Note : Since is used fora point of time.
For is used for a period of time.
Exercise 4
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense (present) of the verbs given in brackets :
1. It ………… outside for half an hour. (hail)
2. The storm ………… since 4 O’clock. (howl)
3. I ………… for the bus since morning. (wait)
4. Since when ………… you ………… in this school ? (read)
5. It ………… not ………… since midnight. (rain)
6. She ………… midnight oil for five years. (burn)
7. I ………… for the examination for one year. (prepare)
8. Malaria ………… in this city since July. (rage)
9. How long ………… you ………… for me ? (wait)
10. The washerman ………… our clothes since 1985. (wash)
Answers:
1. has been hailing
2. has been howling
3. have been waiting
4. have, been reading
5. has, been raining/has, rained
6. has bumt/has been burning
7. have been preparing
8. has been raging
9. have, been waiting/have, waited
10. has been washing
Exercise 5
(For Practice)
Insert the correct form of the verb given in the brackets
1. The boys ……….. a song. (sing)
2. I …………. in the school which is the best in the city. (read)
3. The sun ………….. during the day. (shine)
4. God …………… those who ………….. themselves. (kelp)
5. Farmers …………….. a hard life. (lead)
6. Mr. Ram Lal ……………. us English. (teach)
7. He ……………. his lesson regularly. (learn)
8. The toy ……………… a child happy. (make)
9. He ……………… to bed at 10 pm. (go)
10. You ……………… up at 5 am. (wake)
Exercise 6
(For Practice)
I. Fill in the blanks with correct present tense form of the verbs given in brackets :
1. Water ………… at 100°C. (boil)
2. We ………… a hockey match tomorrow. (play)
3. ………… your brother ………… his account ? (clear)
4. The cattle ………… in the field. (graze)
5. She ………… meat several times. (taste)
II. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs (present tense) given in brackets :
1. There ………… (go) the bell !
2. If you ………… not ………… (obey), you will be punished.
3. ………… you ………… (go) for a walk daily ?
4. The players ………… (warm) themselves up at the moment.
5. The train ………… just ………… (arrive).
III. Supply the correct form of the verbs (present tense) given in brackets :
1. Ask him what he (want).
2. The girls (rehearse) a play for the School Day.
3. She (absent) herself since Monday last.
4. What (make) you laugh ?
5. I (fly) to New York next week.
II. The Past Tense
A. The Past Indefinite Tense
Or
The Simple Past Tense
(Subject + II form of the Verb…)
In the Simple Past (Past Indefinite) Tense the second form of the Verb is used :
as—
He came here yesterday.
‘Did’ is used in the Interrogative and Negative sentences. ‘Did’ is also used to lay emphasis. Only the first form of the Verb is used with ‘did’.
(i) In Interrogative Sentences [‘did is placed before the subject and verb in first form after it ; as—]
(Did + Subject + I form of the Verb…?)
Did you show me your homework ?
(ii) In Negative Sentences [‘did not’ is put after the subject and first form of the verb is used thereafter : as—]
(Subject + did + not + I form of the Verb…)
I did not apply for leave.
Exception—I never told a lie.
(This sentence means—I did not ever tell a lie)
(iii) To lay emphasis
I did try to solve the question but was not able to solve it.
Uses of the Past Indefinite Tense
The Past Indefinite (Simple Past) Tense is used :
(a) To express an action completed in the past with reference to the time of speaking.
I saw many birds in the zoo.
(b) To express habitual or regular action in the Past.
Gandhiji always spoke the truth.
(c) To express an event which occurred at a particular point in the Past.
My father came back home yesterday.
(d) To express an action which occupied a period of time in the Past, but is now ended.
We lived in this house for ten years. (do not live now)
I stayed at the Green Hotel for two months. (not staying now)
(e) To express an action where some word, showing past action (yesterday, ago. last, etc.) is given in the sentence, as,
He received your message yesterday.
I passed the S.S.C. Examination last year.
Mark the correct use of the Past Indefinite Tense in the following sentences.
| Incorrect | Correct |
| 1. He has passed the Secondary School Examination in 1978. | He passed the Secondary School Examination in 1978. |
| 2. They have left for Agra yesterday. | They left for Agra yesterday. |
| 3. She has written a letter to her father last evening. | She wrote a letter to her father last evening. |
| 4. Babar has founded the Mughal Empire. | Babar founded the Mughal Empire. |
Note: The difference in the meaning of the following sentences :
(i) He has worked in this office for five years. (He is still working here)
(ii) He worked in this office for five years. (He is no longer working here)
Exercise 7
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given
1. I ………… your letter this morning. (receive)
2. How many deer ………… you ………… in the zoo ? (see)
3. My father ………… a new house last month. ( busy)
4. Prices ………… by forty per cent last year. (rise)
5. Columbus ………… America. (discover)
6. Thousands of people ………… their lives in the earthquake. (lose)
7. Gangu ………… ten rupees from me. (borrow)
8. When ………… you ………… from Allahabad ? (return)
9. I ………… to her house on foot. (go)
10. A thief ………… into our garage last night. (break)
Answers:
1. received
2. did, see
3. bought
4. rose
5. discovered
6. lost
7. borrowed
8. did, return
9. went
10. broke
B. The Past Continuous Tense
(Subject + was /were + I form of the Verb + ing…)
(i) The Past Continuous Tense denotes an action going on in the past. In order to form Past Continuous Tense we add Present Participle to was or were ; as—
The train was running at full speed.
(ii) In Negative form [‘not’ is placed between the helping verb and the principal verb ; as—]
(Subject + was/were + not + Verb + ing…)
She was not weeping.
(iii) In Interrogative form [the helping verb is placed before the subject ; as—] (Was/were + Subject + Verb + ing + … ?)
Were the sheep grazing in the field?
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
(i) The Past Continuous Tense is used to express an action that was happening in the Past at the time of speaking. The time of the action may or may not be mentioned.
Examples: The old lady was crying at the top of her voice.
They were not making a noise.
(ii) The use of this tense with Simple Past Tense denotes that the previous action was going on when the latter action took place; as—
My mother was cooking the food when I reached home.
Exercise 8
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given Tense)
1. The baby ………… in the room.
2. Children ………… a noise in the class.
3. Why ………… you ………… at her ?
4. We saw the aeroplane while it …………
5. The students ………… their morning prayer when I reached their school.
6. I ………… my beard when the telephone bell rang.
7. My mother ………… when I returned home.
8. The old lady ………… the Gita when the guests arrived. (read)
9. Mother ………… tea for us when the school bus homed. (prepare)
10. She found that the baby ………… bitterly. (cry)
Answers:
1. was weeping
2. were making
3. did, look
4. was taking off
5. were saying
6. was shaving
7. was sleeping
8. was reading
9. was preparing
10. was crying
C. THE PAST PERFECT TENSE
(Subject + had + III form of the Verb )
We often make mistakes while using the Past Perfect Tense. We use ‘had’ at random wherever we view ‘past action’ in a sentence in our mother-tongue.
I had gone to Delhi yesterday.
This sentence should be formed in Simple past.
I went to Delhi yesterday.
The structure of Past Perfect is—
In order to form the Past Perfect Tense we use ‘had’ before the Past Participle (III) form of the Verb.
(i) In Interrogative form [‘Had is used before the subject]
(Had + Subject + not + in form of the Verb + ……… ?)
Had he left when you came ?
(ii) In Negative form [‘not is used after ‘had’]
(Subject + had + not + III form of the Verb + ………… )
I had not seen you before.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
(a) The Past Perfect Tense is used to express an action completed before another action took place ; as—
When he came to me, I had posted the letter.
(b) (i) It is also used to express an unfulfilled action in the past ; as—
If she had worked hard she would have passed.
(ii) It is also used to express an unfulfilled wish in the past ; as—
I wish I had won the election.
(c) To denote the action or event which has been completed before some point of
time.
By afternoon he had completed much work.
Use of Past Indefinite and Past Perfect Tenses in Time Clauses
We can express time by using some ‘time-denoting’ Adverbs or through Adverbial clauses of Time. The combination of two past actions depends upon their mutual relevance.
Examples: I had waited for my friend until he arrived.
After he had sailed many days, the mariner reached the coast.
Exercise 9
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets. (Past Tense)
1. Mohan ………….. already ………….. his breakfast. (take)
2. If she ………….. for the examination she would not have failed. (prepare)
3. The bell ………….. before I reached the school. (go)
4. The patient ………….. before the doctor arrived. (die)
5. She ………….. not ………….. the place before her husband permitted her. (leave)
6. ………….. the child ………….. before his mother returned from office ? (sleep)
7. The rain ………….. when we stepped out of our house. (stop)
8. If you ………….. her, she would have got first division. (help)
9. The cinema show ………….. when I reached the hall. (start’
10. If she ………….. a bus, she would have caught the train. (board)
Answers:
1. has, taken
2. had prepared
3. had gone
4. had died
5. had, left
6. Had, slept
7. had stopped
8. had helped
9. had started
10. had boarded.
D. The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
(Subject + had + been + Present Participle…)
(a) The Past Perfect Continuous Tense expresses an action that had been going on for some time in the past. In order to use this tense we use had been with Present Participle (ing) form of the verb.
Examples: Children had been playing since morning.
(b) The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is also used to express an action that had been going on for some time before another action took place in the past ; as—
Examples: They had been playing chess for two hours when I joined them.
(i) In Interrogative form, ‘had precedes the subject and ‘been’ comes after the subject; as—
Had he been quarrelling with you for some time ?
(ii) In negative form, ‘not’ is placed after ‘had’ and before ‘been’ ; as—
They had not been working on this project for many years.
Exercise 10
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets (Past Tense).
1. She ………….. hard since December. (study)
2. Sarla ………….. her lover for many years. (befool)
3. How long ………….. the two neighbours ………….. when a third one joined them ? (quarrel)
4. I ………….. for four hours when you knocked at my door. (sleep)
5. Tenzing ………….. to climb Everest for many years before he succeeded in his mission. (try)
Answers:
1. had been studying
2. had been befooling
3. had, been quarrelling
4. had slept
5. had been trying.
Exercise 11
(For Practice)
I. Rewrite the following sentences changing the Verbs into the Past Tense :
1. Our hen lays one egg daily.
2. Whenever my mother comes, she brings toys for me.
3. She knows that your brother turns with a tide.
4. Anyone who travels by railway through India can see that the country is well supplied with natural wealth.
5. He behaves nicely at tables, talks gently, remains cheerful, thinks of others, keeps an eye on the company and tries to be pleasant and polite in every way.
II. Rewrite the following sentences changing the Verbs into the Present Tense :
1. No one knew what was in store for him.
2. Work, not worth, shall rule mankind.
3. Why did he abuse you ?
4. Fortunately the fighting was over soon.
5. Meanwhile President Kennedy’s father fell ill.
6. A school bus accident killed scores of children.
III. THE FUTURE TENSE
A. The Simple Future/Future Indefinite Tense
(Shall/ will + Verb)
The Future Indefinite Tense is used to express the action or event which is likely to happen in Future. In this tense we use shall/will between the subject and the first form of the verb. Normally we use ‘shall with pronouns of first person (I, We). In the same way. we use ‘will with the pronouns of second person (you) and third person (he, she, it, they).
(i) In Negative sentences ‘not’ is added after ‘shall/‘will as the case may be ; as— We shall not see the picture today.
(ii) In Interrogative sentences ‘will’/‘shall’ is placed before the subject and first form of the verb after it ; as—
Will you go to college today ?
B. THe Future Continuous Tense
(Will/shall + be + Verb + ing)
The Future Continuous Tense is used to express an event that is expected to take place in the normal course or at some time in the future ; as—
We shall be playing a football match on Sunday.
The new edition of this book will be coming out shortly.
When I reach Calcutta, it will be raining heavily there.
Will you be taking part in the debate ? (Interrogative)
The farmers will not be watering the plants at this time. (Negative)
C. The Future Perfect Tense
(Shall/will + have + III form of the Verb)
(i) The Future Perfect Tense expresses an action which is expected to be completed by a certain time in the Future ; as—
She will have covered half of her journey by Monday next.
(ii) The Future Perfect Tense sometimes expresses the speaker’s belief that something has taken place. In such sentences it does not express the Future ; as—
“You will have discussed the plans how to celebrate the function”, said my mother.
(iii) It is also used for an action which at a given future time will be in the past; as—
In two years’ time (i.e., two years from now) I shall have taken my degree.
Exercise 12
(Solved)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in brackets.
1. The picture ………….. by the time we reach the hall. (start)
2. ………….. you your studies by 2009 ? (finish)
3. The farmers ………….. not ………….. the harvest before September. (reap)
4. I ………….. exercise before the sun rises. (take)
5. He ………….. his lesson by next week.
Answers: (learn)
1. will have started
2. Will, have finished
3. will, have reaped
4. shall have taken
5. will have learnt
D. The Future Perfect Continuous Tense
(Shall/will + have been + Verb + ing)
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to express an action that will have been going on at or before some point of time in the Future ; as—
We shall have been waiting for you for a long time.
Exercise 13
(Solved)
What Are The 16 Tenses In English
I. Rewrite the following sentences changing the Verb into the Future Tense :
1. I reached the station after the train had left.
2. The log of wood broke and they fell into the ditch.
3. They bound his hand and foot and held him fast.
4. I broke the lock open and got into the room.
5. The gardener was watering the plants.
6. You have really committed a blunder.
7. He found her weeping bitterly.
II. Correct the following sentences :
1. He has left for his native village yesterday.
2. I had completed the work.
3. He told me that he has solved all the sums.
4. I informed you about this before.
5. I know you for many years.
6. She had seen a lion in the circus.
7. He is pass in English and is fail in Mathematics.
8. If you help me, I give you a reward.
9. It is raining heavily since a week.
10. The patient died before the doctor arrived.
11. He will meet me as soon as he will return.
12. The teacher punished the boys because they are making a noise.
Answers:
I. 1. I shall reach the station before the train leaves.
2. The log of wood will break and they will fall into the ditch.
3. They will bind his hand and foot and hold him fast.
4. I shall break the lock open and get into the room.
5. The gardener will be watering the plants.
6. You will have really committed a blunder.
7. He will find her weeping bitterly.
II. 1. He left his native village yesterday.
2. I completed the work.
3. He tells me that he has solved all the sums.
4. 1 had informed you about this before.
5. I have known you for many years.
6. She saw a lion in the circus.
7. He has passed in English but failed in Mathematics.
8. If you help me. I will give you a reward.
9. It has been raining heavily for a week.
10. The patient had died before the doctor arrived.
11. He will meet me as soon as he returns.
12. The teacher punished the boys because they were making a noise.
Common Errors In The Use Of Verbs
| Incorrect | Correct | |
| 1. | He is pass in English. | He passes in English. |
| 2. | Bum the lamp. | Light the lamp. |
| 3. | When will you give the test? | When will you take the test? |
| 4. | The teacher will take our test in English next week. | The teacher will give us a test in English next week. |
| 5. | I am ill for four days. | I have been ill for four days. |
| 6. | She gave a speech. | She made a speech. |
| 7. | Our team made two goals. | Our team scored two goals. |
| 8. | I wish I was young again. | I wish I were young again ! |
| 9. | He talks as if he is mad. | He talks as if he were mad. |
| 10. | What make you laugh? | What makes you laugh? |
| 11. | I hanged* my coat on the peg. | I hung my coat on the peg. |
| 12. | The murderer was hung. | The murderer was hanged. |
| 13. | Two and two makes four. | Two and two make four. |
| 14. | They have come this morning. | They came this morning. |
| 15. | He was so thirsty that he drunk all the milk. | He was so thirsty that he drank all the milk. |
| 16. | I hope he will fail. | I fear he will fail. |
| 17. | I saw into the bus, but looked none. | I looked into the bus, but saw none. |
| 18. | He works hard lest he should not fail. | He works hard lest** he should fail. |
| 19. | Our hen has given ten eggs. | Our hen has laid ten eggs. |
| 20. | He fell off the roof and died. | He fell off the roof and was dead. |
* In the past form, ‘Hanged’ is used in the sense of awarding ‘capital punishment’ suspending by the neck until dead.
The murderer will be hanged tomorrow.
He took off his coat and hung it on a peg.
** ‘Not’ is included in ‘lest’. ‘Lest’ = in order that—not.
Exercise 13
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks choosing one word for each blank from the box. You may use a word or phrase more than once.
| knocked, injured, had died was reading, died, was turning sat, slipped, was mowing crossed, arrived. |
1. He ………….. the room and ………….. down in the chair.
2. As he ………….. left on the road, a bus ………….. him down.
3. He ………….. and ………….. his leg.
4. The passenger ………….. a newspaper.
5. He was seventy years old when he …………..
6. The doctor came after the patient …………..
7. I noticed that his hair ………….. grey.
8. When we he ………….. the lawn.
Answers:
1. crossed, sat
2. was turning, knocked
3. slipped, injured
4. was reading
5. died
6. had died
7. was turning
8. arrived, was mowing
Exercise 15
(Solved)
Last night a dozen armed men enter a house. (a) _________
They were arm with sticks. First they (b) _________
attack the owner. When he resisted, he (c) _________
was beat up with the sticks. They (d) _________
loots cash and ornaments. They had (e) _________
lock him in a bathroom. (f) _________
Answers:
(a) enter — entered
(b) arm — armed
(c) attack — attacked
(d) beat — beaten
(e) loots — looted
(f) lock — locked
Exercise 16
(For Practice)
The following passage has not been edited. There is an error in each line. Write the error along with the correction. Do not forget to underline the correction.
A young man from Punjab decide to go (a) _________
to Canada. He meet an agent in Delhi. (b) _________
The agent tell him that he would have (c) _________
to paid rupees seven lacs. The youngman (d) _________
agree to pay the amount. The agent (e) _________
demanded some advance which was also pay. (f) _________
Later, the agent is discovered to be a fraud. (g) _________
Exercise 17
(For Practice)
Rearrange the following to make meaningful sentences :
1. Sudhir / coming / Tuesday / on / is.
2. be given / he / a thrashing / should
3. they / in / the doctor / called
4. the President / the prizes / away / gave
5. I / my friends / a sad farewell / bade
6. elected / President / Gopal / we.
Exercise 18
(For Practice)
Fill in the following blanks with correct tense of the verbs given in the brackets : (Future Tense)
1. Dinesh ………….. for us at the appointed time. (wait)
2. When Sarla calls on me, I ………….. my clothes. (iron)
3. The gardener ………….. the plants next month. (water)
4. Sonu ………….. his lesson tomorrow at this time. (revise)
5. Mohini ………….. tea when you enter her room. (make)
6. The patient ………….. rest when the doctor arrives. (take)
7. The peon ………….. the bell when I reach the school. (ring)
8. Sharda ………….. for Madras this time tomorrow. (leave)
9. We ………….. our courses by the end of January. (complete)
Exercise 19
(For Practice)
Fill in the following blanks writh correct tense of the verbs given in brackets using future tense.
1. They ………….. the sums since morning. (solve)
2. We ………….. in the river for three hours before noon. (bathe)
3. We ………….. our time during examination days. (not waste)
4. The farmers ………….. the fields since 2008. (plough)
5. ………….. he ………….. for you for an hour ? (wait)
6. By next year, I ………….. in Jaipur for seven years. (live)
7. Our school team ………….. the other team for the seventh time. (defeat)
8. She ………….. since 8 A.M. before I reach home at noon. (study)
16 Tenses In English Grammar Chart
Exercise 20
(For Practice)
Fill in the blanks in the following sentences with the simple or the progressive (continuous) form of the verb.
1. The Indians ………….. in India, (live)
2. He ………….. to office every morning, (go)
3. My aunt ………….. with us for a few weeks, (stay)
4. Jack cannot come out to play at the moment as he ………….. his homework, (do)
5. They ………….. to Joshi Math for the summer, (go)
6. A vegetarian never ………….. meat, (eat)
7. Some birds ………….. every year, (migrate)
8. A milliner ………….. ladies’ hats, (sell)
Multiple Choice Questions
Exercise 1
Fill in the blanks in the following sentences using one o f the options from the brackets :
1. A teetotaller ………….. (drink/drinks/drank/drinking) no wine.
2. Do you ………….. (prefer/preferred/preferring/preferable) tea to coffee ?
3. I felt the earth ………….. (slipping/slip /slipped/going) under my feet.
4. I ………….. (think/thought/am thinking/was thinking) you are right.
5. I ………….. (took/taking/taken/have taken) my dinner an hour ago.
6. The train ………….. (did not arrive/will not arrive/has not arrived/had not arrived) yet.
7. If you ………….. (come/came/will come/shall come) in time you will get a seat.
8. T he train had left before we ………….. (reach/reached/had reached/will reach) the station.
9. We could start taking dinner if only John ………….. (is/were/was/are) here.
10. If you ………….. (heat/heated/heating/will heat) the ice it melts.
Answers:
1. drinks
2. prefer
3. slip
4. think
5. took
6. has not arrived
7. come
8. reached
9. were
10. heat
Exercise 2
The underlined words in the following sentences have been wrongly used. Supply the correct word/ words from the options given below each sentence :
Question 1.
Ask him what he want,
(a) wants
(b) wanted
(c) has wanted
(d) wanting
Question 2.
There came the train.
(a) come
(b) comes
(c) has come
(d) had come
Question 3.
The guest have just now,
(a) leaves
(b) left
(c) leaving
(d) has left
Question 4.
I receive your letter this morning.
(a) received
(b) receives
(c) have received
(d) had received
Question 5.
A thief break into that house last night.
(a) breaking
(b) broke
(c) broken
(d) has broken
Question 6.
The bell go before I reached the school.
(a) went
(b) gone
(c) has gone
(d) had gone
Question 7.
If you had run you catch the train.
(a) caught
(b) catching
(c) would have caught
(d) had caught
Question 8.
If you help me. I could have passed.
(a) helping
(b) have helped
(c) had helped
(d) helped
Question 9.
The train go by the time we reach.
(a) went
(b) will go
(c) will be going
(d) will have gon
Question 10.
I is ill for a week.
(a) am
(b) was
(c) have been
(d) had been
English Tenses
Answers:
1. (a) wants
2. (b) comes
3. (d) has left
4. (a) received
5. (b) broke
6. (d) had gone
7. (c) would have caught
8. (c) had helped
9. (d) will have gone
10. (c) have been
16 Tenses In English Grammar Worksheet
We hope the CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Tenses help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Tenses, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.